Decarbonization
Epson is combating climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions in operation (scopes 1 and 2) and across its value chain (scope 3) to help drive a transformation toward a decarbonized future, as envisioned by the Paris Agreement. Epson also contributes to society by developing energy saving products and further developing inkjet technology.
Goal
GHG Emissions Reductions
In Paris Agreement in 2015, a global long-term goal (1.5°C target) was set to pursue efforts to limit global average temperatures to within 1.5°C of pre-industrial levels. We recognize that achieving this goal will mitigate the impacts of climate change and is essential to achieving sustainability and enriching communities. Based on this recognition, Epson has developed GHG emission reduction targets for its value chain, consistent with the global 1.5°C target, toward net-zero in 2050.
In addition to achieving these targets, Epson is taking further steps to absorb and remove carbon to contribute to the realization of a decarbonized society, aiming to achieve net-zero Scope 1+2 emissions in 2030 and carbon negative by 2050.
GHG Emission Reduction Targets and Goals
| Targets approved for SBTi1 (1.5°C target level. All reductions are compared to the baseline year of fiscal 2017)
|
Near-term targets: Reduce total scope 1+2+3 emissions by 55% by 2030 Reduce total scope 1+2 emissions by 90% by 2030 Long-term targets: Reduce total scope 1+2+3 emissions by 90% by 2050 Achieve net-zero by 2050 |
| Goals2 | Achieve net-zero Scope 1+2 emissions by 2030 Achieve carbon negative by 2050 |
1 The Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi) is a corporate climate action organization that helps companies and financial institutions contribute to addressing the climate crisis. The Initiative is developing standards, tools, and guidance to help companies set GHG emission reduction targets consistent with the levels needed to keep global warming below catastrophic levels and achieve net zero by 2050 at the latest.
2 A target approved by SBTi to reduce total emissions by 90% and neutralize remaining emissions through absorption, credits, etc. to achieve net-zero emissions or further decarbonization.
Scope 1: Direct emissions from the use of fuels by business parties
Scope 2: Indirect emissions from energy sources such as electricity
Scope 3: Indirect emissions from the company's entire value chain
Risks & Opportunities (Responding to TCFD)
The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) released its final report in June 2017. The TCFD encourages businesses to publicly disclose their medium- to long-term risks and opportunities related to climate change as financial information. Epson takes this as a call to develop resilient management and corporate health, able to adapt to all sorts of transitions in the face of climate change with impacts of a scope and scale we cannot predict.
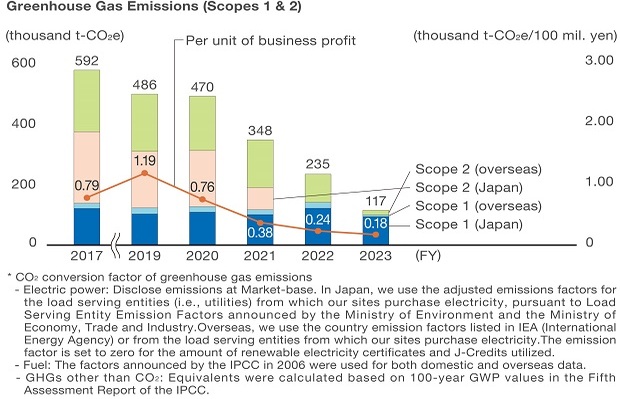
Operational Initiatives (Scopes 1 and 2)
Under a company-wide cross-functional organization, each site is increasing the feasibility of decarbonization by implementing reduction measures such as production innovation, equipment and facilities renewal and investment, and the use of renewable electricity.
Main actions to reduce Scopes 1 and 2 emissions
- Production innovations
- Investment in updated facilities and equipment such as plant infrastructure, scrubbers, and solar power systems
- Use of renewable electricity: Procurement of renewable electricity that uses local natural resources, etc.
- Other reductions to be achieved by power utilities reducing their GHG emissions factors
Carbon Pricing
Carbon pricing, an instrument that captures the costs of GHG emissions across society, is seen as a way to spur action and innovation in support of lower carbon emissions. Epson prepared payback period criteria and guidelines that incorporate carbon pricing principles to evaluate (study the feasibility of) potential investments for reducing GHG emissions. They were introduced on a trial basis in FY2018 and were formally adopted in 2020.
2023 Overview
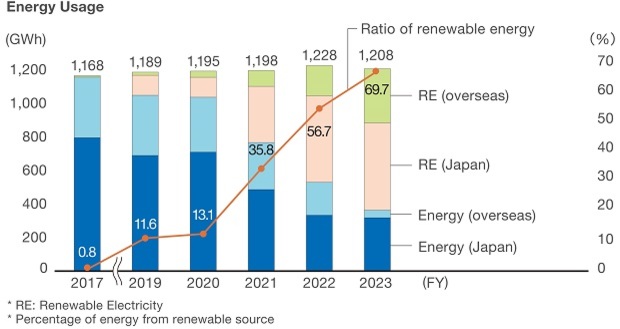
In addition to promoting energy-saving activities at each of its sites, Epson has been promoting the use of renewable energy sources; in fiscal 2023, the ratio of renewable energy sources, which previously accounted for less than 1%, was increased to approximately 69% (96% on an electricity basis). Although energy use is expected to increase in order to realize the Medium-Term Management Plan, Epson will continue to focus on reduction measures, including production innovation, renewable electricity together with the use of electricity, to achieve its goals.
Related link
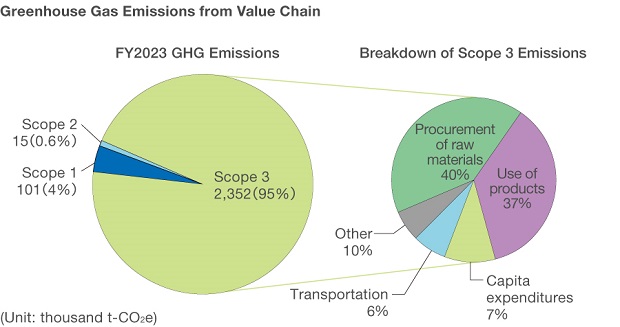
Value Chain Initiatives (Scope 3)
Epson is actively working to reduce emissions from business activities (Scopes 1 and 2), but when viewed in the value chain, other indirect emissions (Scope 3) account for more than the direct and indirect emissions from Epson's production site and other sources. Of these, the largest impacts are from the procurement of raw materials (Category 1: purchased goods and services) and the use phase of products (Category 11: use of products sold).
In light of this situation, Epson is promoting emission reduction measures throughout the entire value chain, including logistics, in addition to environmentally friendly raw materials procurement and improvement of energy-saving performance of its products.

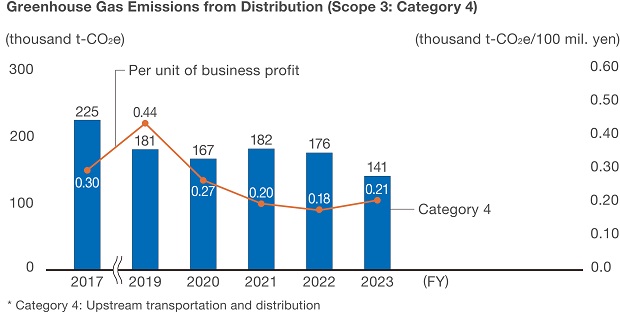
Logistics Initiatives
Epson is reducing GHG emissions by increasing the efficiency of product, part, and waste transportation. We are making products smaller (which increases shipping efficiency), rethinking our logistics centers, innovating the loading and packing processes (to boost loading efficiency), and reconsidering shipment departure and arrival frequencies and number of trips.
Cooperation with Suppliers
Epson and its suppliers can help address societal challenges and achieve sustainability by aligning their approach to supply chain CSR.
Related link
Avoided Emissions
In addition to reducing its own GHG emissions and using resources appropriately, Epson aims to mitigate customers’ environmental impact through its products and services. By providing and promoting products and services that are environmental impact lower than the conventional products commonly used in the world, Epson will contribute to the reduction of environmental impact in society as a whole. One indicator of such contribution is avoided emissions.
Based on the guidance published by the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) and confirmed by a third-party organization, Epson calculated that the emissions avoided through the replacement of laser printers with Epson's inkjet printers in fiscal year 2023 amount to 15.1 thousand t-CO2e1 .
1 Based on the calculation method confirmed by Mizuho Research & Technologies, Ltd., the value is obtained by multiplying the difference between the weighted average of the publicly available lifetime CO2 emissions of major laser printers in the global market and the lifetime CO2 emissions of Epson's A3 color inkjet printer by the number of Epson A3 color inkjet printers sold in a given fiscal year.
Related link
Use of Renewable Electricity
The use of renewable electricity is a key means by which Epson seeks to reach its goal of achieving decarbonization. In line with this, Epson declared, in March 2021, that it would switch to 100% renewable electricity to meet the electricity needs at all Epson Group sites1 around the world by 2023. In November 2021, the switch was completed in Japan. The global switch to renewable electricity was completed on schedule in December 2023. The Epson Group consumes approximately 872 GWh2 of electricity per year. By sourcing renewables to cover this demand, Epson expects to reduce its annual CO2 emissions by approximately 400,000 tonnes.
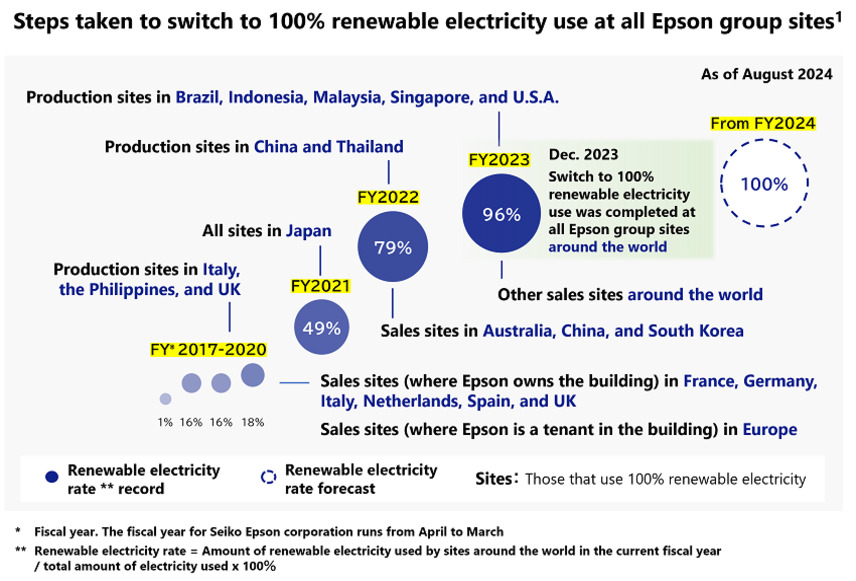
1 Excludes some sales sites and leased properties where the amount of electricity consumed cannot be determined.
2 For the fiscal year 2023, the results include cogeneration systems (CGS) electricity and self-generated electricity. Since it is difficult to procure renewable energy fuels or green gas certificates that meets the RE100 technical criteria, we have achieved 100% renewable electricity by voluntarily applying renewable energy certificates equivalent to the amount of electricity used.
Epson Transitions to 100% Renewable Electricity at All Group Sites Worldwide
How manufacturers can transition to 100% renewable electricity
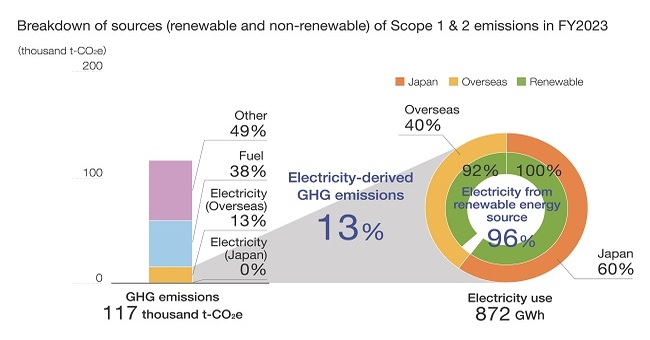
Scope1 & 2 emissions and electricity consumption in FY2023
More than 70% of Epson's GHG emissions came from the consumption of electricity in fiscal 2017. As a result of our prior efforts to achieve decarbonization by switching to renewable electricity we use, the ratio of GHG emissions from electricity declined to about 10% in fiscal 2023. At home and abroad, we have increased the percentage of renewable energy to 96% of electricity usage by selecting the optimal renewable electricity in each region, such as hydropower and wind power, and by proactively investing in on-site electricity generation.
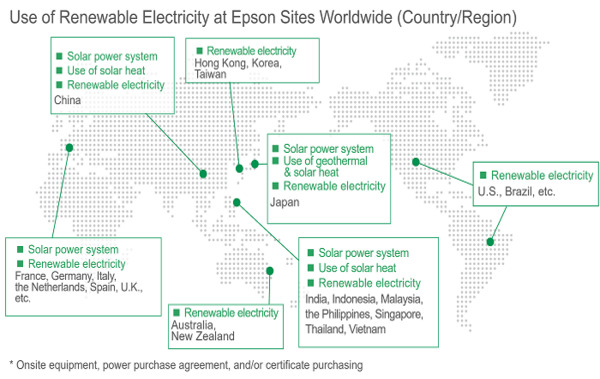
Transitioning to Renewable Energy at Epson's Global Sites
In Japan, Epson purchases Shinshu Green Electricity, CO2-free value-added electric power produced locally with abundant water sources in Nagano Prefecture using Nagano Prefectural hydroelectric power. This is both reducing Epson's GHG emissions and increasing local consumption of locally produced energy. In the Tohoku area, where Epson has a semiconductor fabrication plant and which accounts for about half of Epson's domestic electricity consumption, Epson uses another CO2-free value-added electric power to reduce GHG emission from electricity usage. In November 2021, Epson completed the transition to 100% renewable electricity for all its domestic sites in Japan.
Our overseas production and sales sites have also completed the transition to using 100% renewable electricity in December 2023. In addition to generating electricity with a rooftop mega-solar power plant, our production site in the Philippines switched to a mix of geothermal and hydroelectric power in January 2021. In addition, our production site in Bekasi, Indonesia, began using biomass power generation in July 2022. The procurement of geothermal power, which is being actively developed by taking advantage of the resources of volcanic islands, and sustainable biomass power using Palm Kernel Shells (PKS; a byproduct of the palm oil production process) and wood chips as fuel, are examples of energy use that aligns with regional characteristics.
Case of onsite solar power generation




1 Power Purchase Agreement: Onsite Solar Power Generation Service
Support for Recommendations to Expand the Use of Renewable Energy
The use of renewable energy (energy from natural sources) is one of the most effective ways to reduce GHG emissions. Accordingly, Epson is implementing plans to expand its use of renewable energy long-term. However, there are obstacles to expanding renewable energy use, including costs and supply limitations in some regions. Recognizing that there is nothing one company alone can do about these obstacles, Epson decided to declare its support for the important policy recommendations below as one solution. The realization of these recommendations will make it easier to take actions that minimize the impact on future climate change.
Coordinated global action is essential to combat climate change. We at Epson will therefore continue our efforts toward decarbonization, including by supporting future such recommendations. When deciding whether to join or continue our association with industry groups, we check whether the group's climate change initiatives are aligned with Epson's own policies.
| Month/Year | Recommendations | Secretariats |
|---|---|---|
| Jul. 2024 | Call for an ambitious 2035 target that is consistent with the 1.5℃ goal | Japan Climate Initiative (JCI) |
| Jun. 2023 | Issues and Recommendations on Renewable Electricity Procurement | Renewable Energy Institute |
| Apr. 2023 | Call for accelerating the deployment of renewable energy and introducing effective carbon pricing | Japan Climate Initiative (JCI) |
| Jun. 2022 | Call for accelerating renewable energy deployment | Japan Climate Initiative (JCI) |
| Apr. 2021 | Calling for an Ambitious 2030 Target for Japan to Realize the Paris Agreement Goal | Japan Climate Initiative (JCI) |
| Jan. 2021 |
Calling on the Japanese government to raise its 2030 renewable energy target to 40-50% |
Japan Climate Initiative (JCI) |
| Aug. 2020 |
Making Japan a Nation where Renewable Electricity is Easily Accessed: Three Strategies and Nine Policies Sought by Corporations Engaged in Climate Action |
Renewable Energy Institute CDP Worldwide-Japan WWF Japan |
Related link
Global Environmental Data
How manufacturers can transition to 100% renewable electricity
Epson Transitions to 100% Renewable Electricity at All Group Sites Worldwide