Environmental technology development
Goal
Developing environmental technology based on societal issues to foster the circular economy
We have identified four materialities in establishing the Epson 25 Renewed corporate vision. One of these is achieving sustainability in a circular economy. To realize this, we are focusing on developing technologies that contribute to closing the resource loop without relying on underground resources and aim for carbon negative. Additionally, we are actively promoting co-creation with partners to develop new solutions that contribute to reducing environmental impact, aiming to create new business opportunities.
For example, through material technologies such as Dry Fiber Technology (DFT) and Metal Powder Manufacturing Technology, we aim to replace underground resources with above-ground resources by utilizing unused materials and recycled materials.
Additionally, to achieve carbon negative, we are developing CO2 absorption technologies to address unavoidable residual greenhouse gas emissions.
Dry Fiber Technology (DFT)
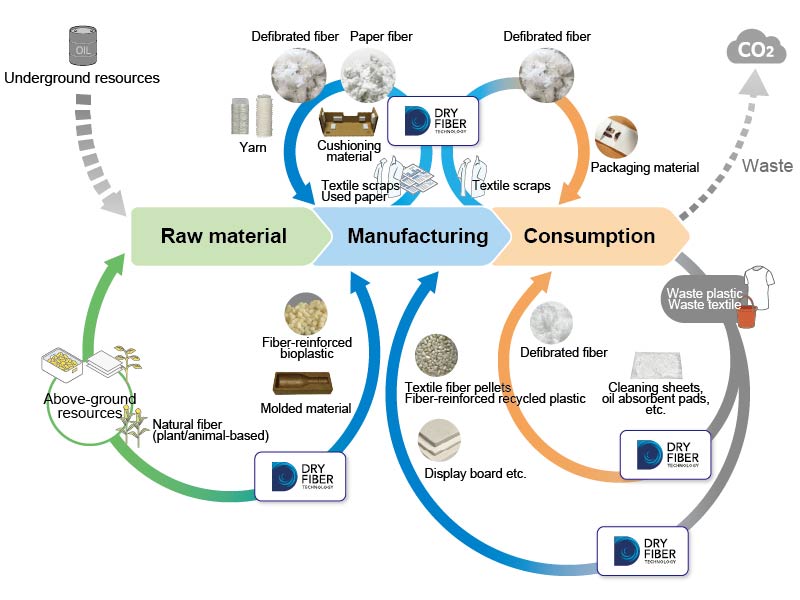
Closing the resource loop by recycling paper and textile fibers
Dry Fiber Technology is a defibration technology used in Epson's PaperLab dry-process office papermaking systems. We are evolving Dry Fiber Technology and expanding its use in-house to create sound-absorbing and cushioning materials for equipment from used paper. We are also developing new internal applications for cotton mill ends from clothing.
We have also entered into a joint development agreement with the Hong Kong Research Institute of Textiles and Apparel limited (HKRITA) to establish a process for defibrating elastic blended fabrics and tightly woven fabrics. This will enable the extraction of new recycled fibers from functional clothing, sheets, and dress shirts, as well as from factory mill ends, unsold items of clothing, and unwanted apparel.

Accelerating the social implementation of composite plastics for a circular economy in collaboration with Tohoku University
Using bioplastics and recycled plastics instead of virgin plastics is crucial for a circular economy. However, bioplastics often have lower mechanical strength and durability than virgin plastic, which limits their usage to certain applications.
Epson has been collaborating with Tohoku University under a comprehensive partnership agreement since 2006, engaging in systematic research and development as well as talent cultivation through industry-academia cooperation. Joint research on fiber-reinforced plastics, based on Dry Fiber Technology, is one of the efforts. In August 2023, the establishment of the "Sustainable Materials Co-Creation Research Institute" aims to accelerate research and development, as well as social implementation, of foundational technologies for cellulose fiber-reinforced bioplastics and recycled plastics, which serve as sustainable materials to drive the circular economy.

The development of composite plastics using defibrated cellulose or fabric has been adopted as a sub-project under the "Construction of a Circular Economy System," which is part of the Cross-Ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP)1 Phase 3, led by the Cabinet Office. (July 2023)
1 A national program led by the Council for Science, Technology, and Innovation (CSTI) aims to achieve scientific and technological innovation, transcending the boundaries of ministries and conventional fields.

Related Information
Related Information
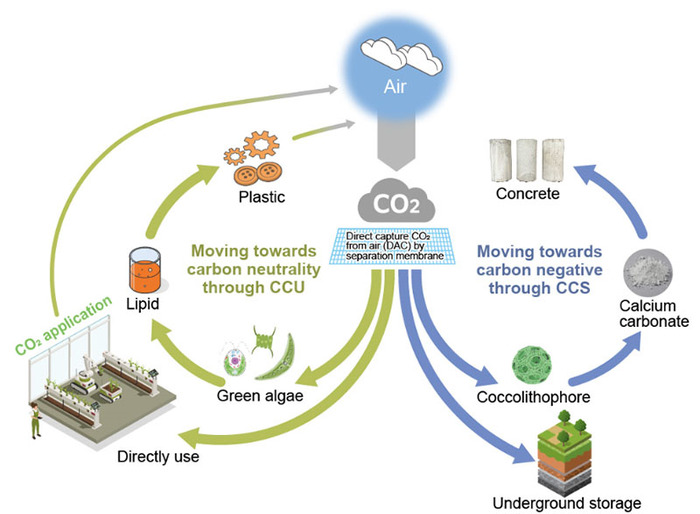
CO2 Absorption Technology
Epson aims to establish CO2 absorption technologies that can offset its own residual CO2 emissions in pursuit of carbon negative, as outlined in its Environmental Vision 2050.
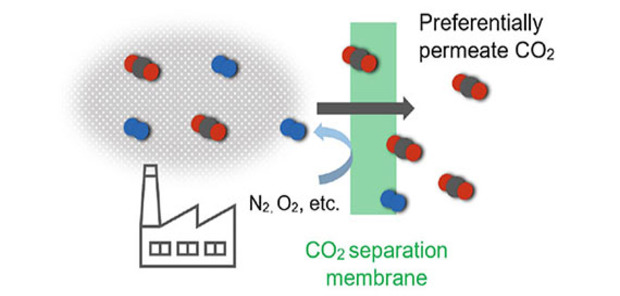
CO2 separation membrane based on Epson's proprietary technologies
Epson is developing separation membrane that preferentially transmit CO2 based on several proprietary technologies, such as thin film technology from inkjet heads. In the future, we aim to achieve high-efficiency CO2 capture with compact, low-energy systems.
Biological carbon fixation
Epson is working on the development of CO2 absorption technologies using microalgae. For CCS1, we focus on coccolithophores, which synthesize calcium carbonate. Through the optimization of cultivation conditions and the application of various breeding technologies, In our laboratory, we have succeeded in achieving fixation that is 70 times what forests2 that is 70 times what forests can, in terms of CO2. For CCU3, we are developing technologies that utilize green algae. Going forward, we aim to enhance CO2 fixation efficiency and ultimately pursue the utilization of CO2 as a valuable resource.

1 CCS (Carbon dioxide Capture and Storage): A technology that separates and collects CO 2 emitted from power plants, factories, etc., from other gases, and stores it underground, etc.
2 Data from the National Forestry Research Institute, Forestry and Forest Products Research Institute, Japan
3 CCU (Carbon dioxide Capture and Utilization): A process in which separated and collected CO 2 is directly used in agriculture, etc., or converted into fuel, etc.
Metal Powder Manufacturing Technology
Recycling Metal Materials in the Epson Group with Original Metal Powder Manufacturing Technology
Epson Atmix Corporation is using its metal melting and atomizing process technologies to produce metal powder products. In February 2020, the company began taking silicon wafers that were used in Epson's semiconductor fabrication business and producing metal powder from them. This reuse of wafers reduces Epson's waste, CO2 emissions, and use of underground resources such as virgin silicon. By the end of the 2021 fiscal year, Epson Atmix had recycled 8.5 tonnes' worth of silicon wafers. The company will continue to search for other materials that could potentially be upcycled into high-performance metal powders.

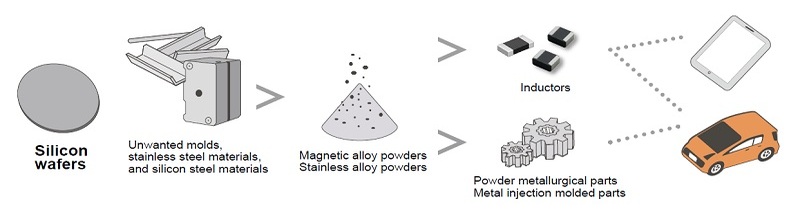
Metal refining plant that converts unwanted metals into material resources
In June 2025, Epson Atmix launched operatiions at a new plant to recycle used metals from the Epson Group's own operations and the local community. The recycled metals are used as raw materials for metal powder products. With the operation of this new plant, virgin raw materials such as blast furnace pure iron will be replaced with recycled metal materials, conserving underground resources and reducing CO₂ emissions.




