Closed Resource Loop
In pursuit of a circular economy, Epson is working to reduce resource use and eliminating waste emission form plants and offices, while promoting a shift to sustainable resources. In addition, we will contribute to resource-circulating society as a whole through technology.
- Goal
- Reduce Total Resource Inputs
- Eliminate Waste
- Replace with Sustainable Resources
- Contribution to Paper Circulation
Goal
Underground Resource1 Free
Resource use often involves environmental impact In particular, fossil fuels and other underground resources cause greenhouse gases (GHGs) and harmful substances at each stage of extraction, utilization, and disposal, with negative impacts on human health. As long as we depend on underground resources, we cannot achieve a decarbonized society, nor can we achieve sustainability and enrich communities.
Epson is committed to reducing the total volume of resource inputs and replacing all resources with sustainable resource2 such as closed loop resources by 2050 to reduce waste. Through such efforts, we aim to realize a sustainable society by using underground resource free.
Main actions to become underground resource free
- Reduce total resource inputs by creating compact and lightweight designs, extended product life, product recycling, etc.
- Eliminate waste by minimizing production losses, reducing inventory, eliminating disposal in landfills, etc.
- Switch to sustainable resources such as recycled materials and biomass materials.
Target
2030: Sustainable resource rate3 50%
2050: Sustainable resource rate 100%
FY2024 Result
Sustainable resource rate: 33%
1 Non-renewable resources such as oil and metals.
2 Renewable resources, closed loop resources and less-depletable resources.
3 The proportion of sustainable resources (renewable resources + closed loop resources + less-depletable resources) to raw materials.
Reduce Total Resource Inputs
Compact and Lightweight Design
Epson seeks to deliver more customer value with fewer resources. By reducing waste through smaller and lighter product designs, we focus our resources on delivering the value that is truly required.
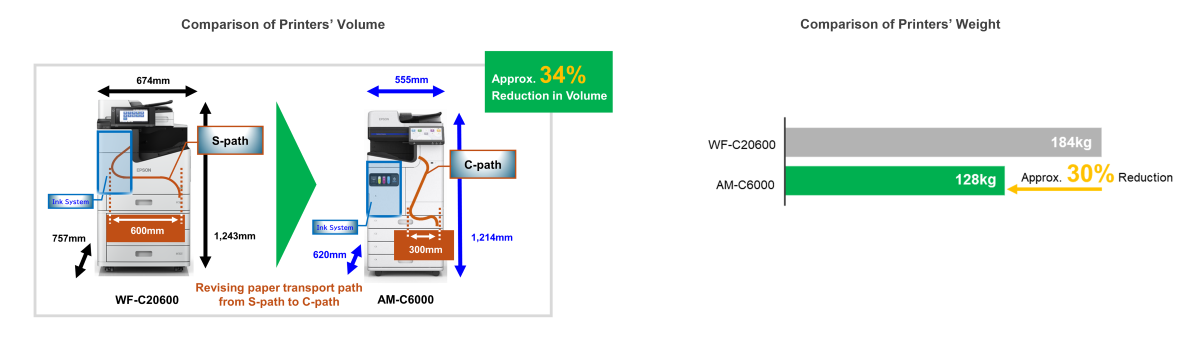
Case Study 1: Business Inkjet Printer
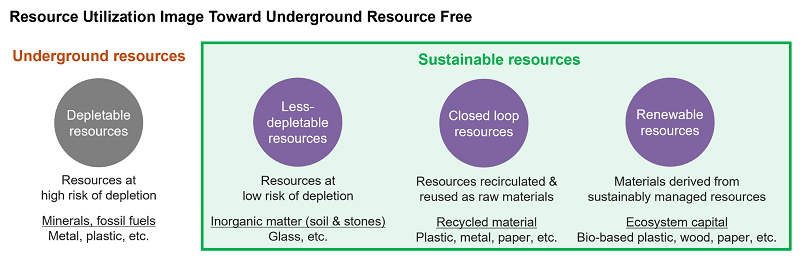
Compared to its predecessor, the WF-C20600, the AM-C6000 A3 color line inkjet MFP has been made smaller and lighter by revising the paper transport path of the machine and reducing the thickness of the frame plate. As a result, the AM-C6000 is approximately 30% lighter and 34% smaller in volume than its predecessor, while maintaining the same 60-page/minute printing speed, enabling installation in confined spaces.
Case Study 2: Business Projectors
The EB-PU22/PU21 series of high-brightness business projectors are approximately 60% smaller and 50% lighter than conventional models, while maintaining 20,000 lumens of brightness, enabled by a unique liquid cooling system and an optimized structure. It reduces the burden of carrying in and installation at events, large auditoriums, gymnasiums, etc.

1 Comparison of size (W x D x H) of the following products, including protruding parts but excluding the lens.
EB-PU2220S: 586 x 492 x 218 mm / EB-L20000U: 620 x 790 x 358.5 mm
2 Comparison of weights of the following products, excluding the lens.
EB-PU2220S: approx. 24.4kg / EB-L20000U: approx. 49.6kg
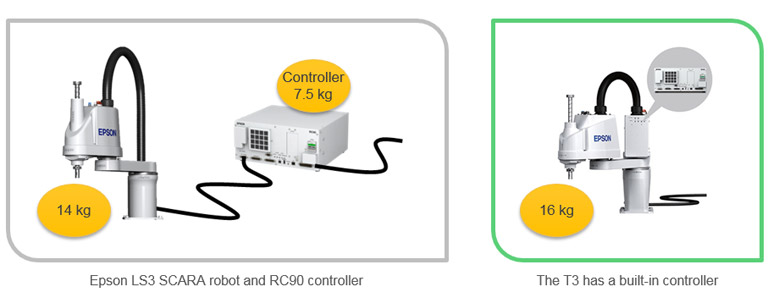
Case Study 3: Industrial Use SCARA robot
In the industrial SCARA robot T3, the controller has been made smaller and lighter, enabling it to be built into the main unit. This reduces the mass by approximately 25% compared to previous models in which the controller and main unit were installed separately, while also reducing complex wiring and increasing installation flexibility.
Reuse and Recycle
To maximize the use of resources once they have been utilized, Epson is promoting the recycling of resources used for the product itself and consumables by providing product repair and maintenance services and promoting collection, recycling, and refurbishing initiatives in countries and regions around the world. In addition to reducing the use of new resources, we are working to create recycled resources throughout society through collaboration with our customers, industry, and local communities to expand the resource reuse and recycling loop.
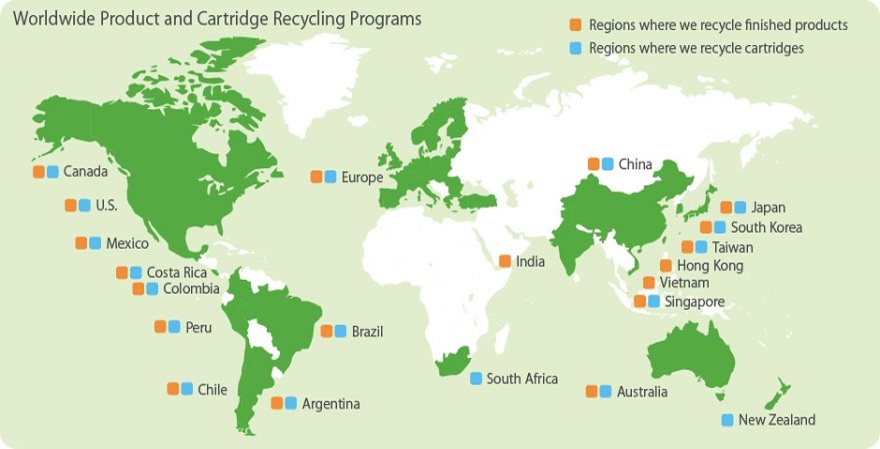
Epson 360°
Epson promotes initiatives to close the resource loop around the world, tailored to local conditions, under Epson 360°.

Eliminate Waste
Epson is working toward zero emissions by reducing generated business waste and using recycled materials.
Wastes are generated in our production processes, offices, and operations. Wherever possible, we reduce, reuse, and recycle these wastes on-site. Plastic runners from molding processes are recycled, for example. The remaining wastes, including valuable wastes, are recycled by a contractor. We carefully sort and separate wastes and select the best available recycling methods and contractors for each type. We will continue to reduce wastes and to work for general improvement in waste processing methods, including by allying with recyclers.
To help combat pollution from oceanic plastic wastes, Epson sales companies in Europe banned disposable cups and other single-use plastics in their office buildings in April 2019.
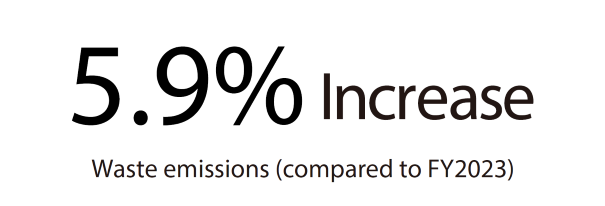
2024 Overview
Target: No more than last fiscal year's 31.6k tons. (Actions were carried out using control metrics benchmarked against the previous year’s waste level.)
Result: 33.5k tons (5.9% increase from the previous year)
* The increase in the amount of waste discharged was due to an increase in the amount of raw materials used in production. However, the amount of waste per unit of raw materials used remained the same as the previous year.
Replace with Sustainable Resources
Adoption of Recycled Plastics
Because plastics are durable, lightweight, and easy to mold, they are used in a wide variety of products and have become an indispensable material in our daily lives. However, most of them are made from petroleum, an underground resource, and GHG and other environmental impact are generated in the process of mining and manufacturing.
Epson is working to reduce the use of petroleum-based plastics through the use of recycled plastics in its products.

* The ratio refers to the proportion of recycled material in the total mass of plastic used. The mass is calculated considering the ratio of recycled materials, and the content may vary depending on procurement conditions.
For product information, see:
Mini PC, Business Projector, Large Format Printer, A3 Inkjet MFP, A4 Document Scanner
* The high-capacity ink tank printer (ET-4810 series) is a model for overseas markets only.
Use of Paper Materials and Closed Loop Resources in Packaging Materials
Many of the packaging materials used to carefully deliver products to customers are made from petroleum-derived materials, an underground resource. Epson is working to replace such materials with paper-based packaging materials.
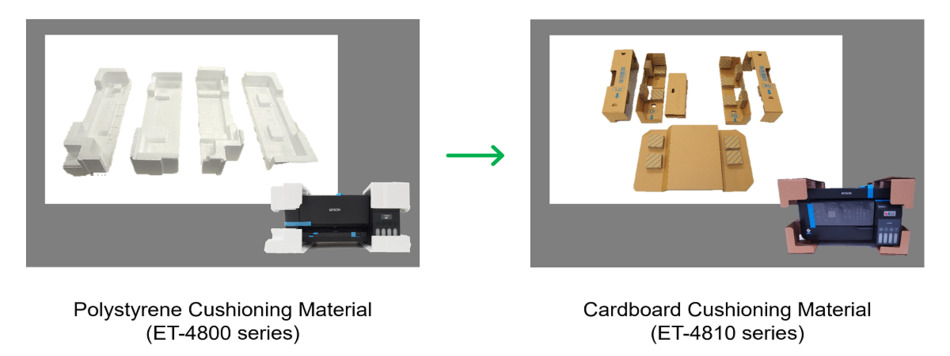
Case Study 1: High-capacity Ink Tank Printer
High-capacity ink tank printer ET-4810 series uses cardboard, a paper-based product, as cushioning material instead of traditional polystyrene cushioning materials. Furthermore, the cardboard contains over 80% recycled material. Additionally, the polypropylene tape used to protect the product during transport has been replaced with paper tape.
Case Study 2: Business Projector
In the EB-L890E series of business projectors, cushioning material has been converted from traditional polystyrene to molded
pulp with a 100% recycled material usage rate. In addition, more than 80% of the cardboard used for the packaging box is made of
recycled materials.

Case Study 3: Watches
Epson has applied its proprietary Dry Fiber Technology to develop a new packaging material made from the scraps generated during the sewing process of cotton clothing, which is used as a packaging material for for Epson watch products.

Contribution to Paper Circulation
There are many situations in which the value of paper media is important from the perspectives of visibility, portability, and preservation. Epson strives to supporting such values while contributing to the sustainable use of paper resources.
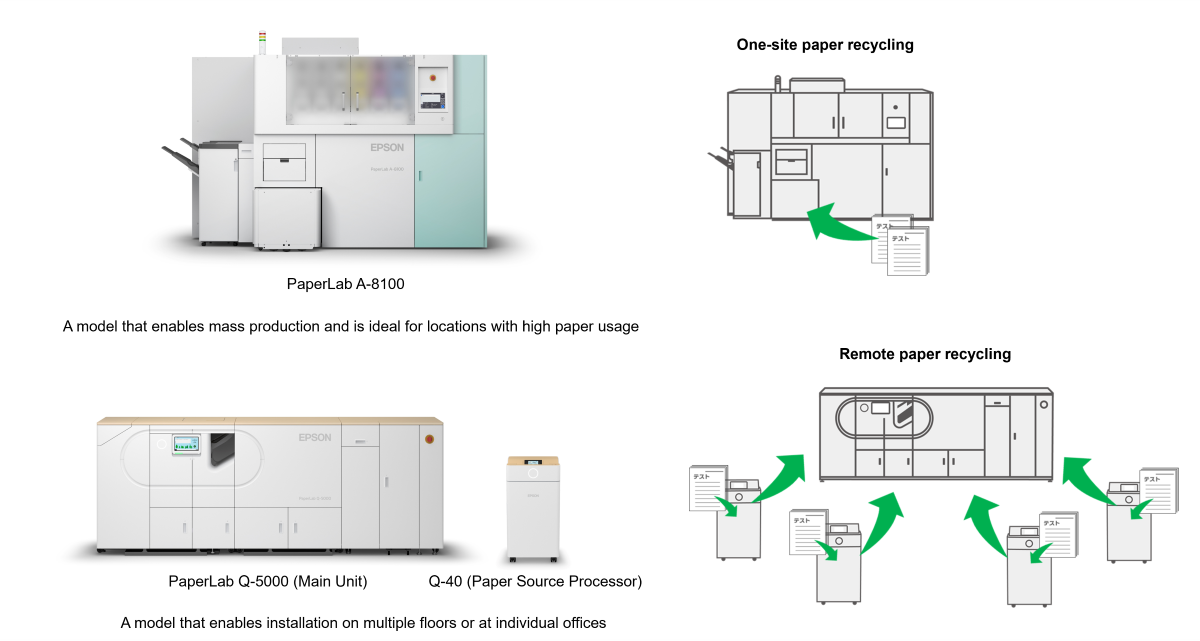
The PaperLab, a dry-process office papermaking machine, is a product that can recycle used copier paper into new paper. Epson proprietary "Dry Fiber Technology" enables on-site papermaking with almost no water required1. Utilizing PaperLab reduces environmental impact of paper production, such as the consumption of forest and water resources and GHG emissions, and also contributes to the preservation of biodiversity.
The PaperLab Q-5000, which was launched in March 2025, is a compact model that can be used in a wider range of situations by local governments, companies, etc. When combined with the Paper Source Processor Q-40, it enables the collection and recycling of waste paper while maintaining confidentiality, promoting the circulation of paper resources within corporate groups and local communities.
1 A small amount of water is used to maintain a humidity inside the system.

Reducing Water Consumption
Uses almost no water in the papermaking process. By reducing water consumption compared to standard copier paper2, it helps mitigate the global issue of water resource scarcity.
2 Refers to standard paper distributed in Japan.

Using Forest Resources Effectively
Used copier paper is recycled into new copier paper, without using any new wood resources. This process effectively utilizes wood as an ecosystem capital and contributes to the reuse of resources that have been used once. Additionally, the new paper produced by PaperLab is made from 100% recycled paper, complying with the R100 mark as specified by the 3R Activities Promotion Forum.![]()

Reducing CO2 emissions
The PaperLab A-8100 enables local recycling of office and community waste paper into new paper products, thereby reducing CO2 emissions associated with the transportation of waste paper for general recycling. Additionally, by using carbon offsets, the CO2 emissions generated throughout the lifecycle of the PaperLab A-8100 are effectively reduced to net-zero. (Carbon offsetting has been certified by a third-party organization.)

Raising Awareness
The fact that new paper can be made on-site is a pleasant surprise for workplace employees, who become more eco-aware and interested in taking other environmental actions. Witnessing the moment new paper is made may also sparks the interest of children, potentially giving them ideas for ways to use science and technology to solve environmental problems. Furthermore, by using PaperLab paper for external documents, business cards, and promotional items, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to environmental responsibility and enhance their image.
Received the Excellence Award at the Green Purchasing Award
Epson was recognized for its value creation efforts with its PaperLab dry-process office papermaking machine, receiving the Excellence Award in thelarge company category at the 26th Green Purchasing Award. This awardrecognizes PaperLab's efforts to contribute to the realization of a sustainablesociety. (December 2025)
[Evaluation points]
The company's proprietary Dry fiber technology has made it possible to recyclecopier paper generated within the office horizontally, and compared toconventional recycled paper manufacturing, it has led to a reduction inenvironmental impact, including CO2 emissions and the use of water and woodresources, which is commendable. Furthermore, the company's promotion ofthe visualization of environmental information, which has led to the motivationand environmental education of users themselves, is an exemplary initiativethat can be emulated elsewhere.

Internal Case Study
Epson actively utilizes PaperLab to promote the reuse of paper used within the company. The company primarily uses recycled paper for its business paper, including for employee business cards. Epson also donates notebooks made from paper recycled from wastepaper within the company to elementary and junior high schools. This initiative not only raises awareness of the importance of paper recycling among children, but also contributes to raising awareness of Epson.
The paper recycling work is carried out by employees of Epson Mizube Corporation, a special subsidiary, and the expansion of job scope has increased opportunities for employees with disabilities to play an active role.

Epson uses PaperLab extensively to recycle and reproduce paper used on its own sites. The recycled paper is primarily used for business purposes, including employee business cards. Additionally, Epson donates notebooks made from recycled paper used in-house to elementary and middle schools. Through this initiative, Epson not only raises awareness about paper recycling among children but also enhances its own brand recognition.
The paper recycling work is carried out by employees of Epson Mizube Corporation, a special subsidiary, which provides opportunities for employees with disabilities to expand their roles and play an active part within the organization.