Environmental History

Harmony, collaboration, and environmental commitment
Epson was founded in 1942 in Suwa, a city located in the rich natural environment of Nagano Prefecture. Harmonious co-existence with the communities in which we operate has long been a cornerstone of the company, and even as our operations have expanded globally, our culture of respect for the environment has never wavered. We demonstrated this in 1988, when Epson became the world's first company to announce that it would eliminate ozone-depleting chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) from its operations. We demonstrated this again by sharing our accumulated technical expertise under the banner of "collaboration before competition." We will maintain a high level of environmental action because, as stated in the Management Philosophy, Epson aims to be a progressive company, trusted throughout the world because of our commitment to environmental conservation.
1942-1979
1942- Pollution Control
Epson began treating wastewater discharged from its site so as to avoid polluting nearby Lake Suwa. In the 1970s, as pollution became a social issue, Epson stepped up its pollution control efforts and established tough new internal environmental standards with stricter water quality limits than required by legislation.

1980-1989
1983 Energy Saving Programs
Since 1980 Epson has carried out programs to save energy by setting energy reduction targets, conducting site energy patrols, installing energy-efficient equipment, and much more. In 1983, the Shoen Plant (now part of the Hirooka office) installed a system with microcontrollers to control lighting fixtures within the factory. The dramatic energy savings that resulted prompted the Illuminating Engineering Institute of Japan to recognize the Shoen Plant with a Good Lighting Award.


1988 CFC-Free Declaration
In 1988, a year that would become the first benchmark year for Epson's environmental programs, Epson became the world's first company to announce that it would completely phase out the use of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) in its global operations. Thanks to an intensive Epson Group-wide effort to eliminate these ozone-depleting substances, we became CFC-free in Japan in 1992 and worldwide the following year.

1990-1999
1991 Cleaning Center
After quickly establishing CFC-free technology, Epson actively supported the efforts of partner companies (outside and on-site contractors) to eliminate the use of CFCs. As part of this effort, Epson set up a shared, CFC-free cleaning center in the former Shimauchi Plant and invited partners to use it.

1992 CFC-Elimination Program Recognition
In 1992 Epson received the first of six consecutive Stratospheric Ozone Protection Awards (both Corporate and Individual Awards) from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in recognition of the company's CFC-elimination program and individual accomplishments therein.
Tsuneya Nakamura, then Chairman of Seiko Epson, commented at the time, "When it became clear that CFCs were damaging the ozone layer, we quickly made a decision to phase them out of our operations. At first, I didn't think the decision was that big of a deal. Only later, when we were selected for this honor, did it dawn on me what we had accomplished.

1993 Local Programs Go Global
Volunteer programs sprouted up across the Epson Group to foster harmony with local communities. In 1993, Epson America, Inc. (EAI) won a Waste Reduction Award from the state of California for its volunteer coastal cleanup program as well as its waste reduction efforts.

1998 The Second Environmental Benchmark Year
In 1998, a decade after the launch of the CFC elimination program and the year that Epson uses as its second environmental benchmark year, Epson established a general environmental action plan for addressing a range of environmental problems and formed six expert committees.
・Environmental Product Committee
・Energy Saving Committee
・Zero Emissions Committee
・Product Recycling Committee
・Chemical Substance Control Committee
・Green Purchasing Committee

1999 Began Publishing Environmental Reports
In 1999 Epson began publishing an annual environmental report to inform the public of its environmental actions and to get public feedback that could be used to help shape future actions. In 2003 we began publishing an annual Sustainability Report that covers not only our environmental actions but also our social programs.

2000-2009
2000 Energy Patrols
In 2000, in response to requests from local businesses and organizations looking for ways to save energy at their own sites, Epson teamed up with some other companies operating in Nagano to form the Suwa Regional Energy Patrol Team. The team visits local businesses, offices, and other facilities to assess their energy use and recommend ways to reduce their energy consumption. In 2005, as the benefits of the program gained broader recognition, a new Shinshu Energy Patrol Team was formed to provide expanded coverage over all of Nagano Prefecture. A similar program was launched in Taiwan in 2010.

2000 Reforestation Project Support
As a way of contributing to Indonesia, a country where Epson has manufacturing operations, Epson established a reforestation program on Kalimantan, an island that has been rapidly losing its tropical rainforests. Enlisting the help of The Japan International Forestry Promotion & Cooperation Center and working closely with the Indonesian government, Epson replanted and maintained the "Epson Forest," a roughly 300 hectare area, up until 2008. By adopting an agroforestry approach, wherein agricultural crops are planted along with trees, this project not only restored a forest in decline but also improved the lives of local inhabitants.

2001 ISO 14001 Certification
Epson was quick to acquire certification for compliance with ISO 14001 as a way to help ensure the continuation and effectiveness of its environmental programs.
In 1995 U.K. affiliate Epson Telford Ltd. (ETL) earned certification for BS7750 (a British Standard for environmental management systems on which ISO 14001 is based). By 2001, all of Epson's major manufacturing and non-manufacturing sites around the globe had acquired ISO14001 certification.

2001 Epson Ecology Labels
In 2000 Epson began the Epson Ecology Label Program. Under this program, we used labels to provide consumers with information about the environmental attributes (self-declared) of Epson products and to promote the creation of eco-conscious products. The LP-9400 (EPL-N7000 in some regions) page printer, released in 2001, was the first product to qualify for a label.

2003 Green Purchasing of Production Materials
We started a standardized, global program to guarantee that certain banned substances are kept out of our supply chain. This program serves to assure that the parts and raw materials procured by Epson Group companies anywhere in the world meet criteria published in the Epson Group Green Purchasing Standard for Production Materials.

2003 Zero Emissions Program
We launched a "zero emissions" program in 1997. The goals of this program are to recycle 100% of the emissions generated by our business activities (Level 1) and to reduce our total emissions (Level 2). By 2003 every Epson site around the world had achieved Level 1. Presently, we are working to reduce the volume of waste itself and to achieve a higher level of recycling.

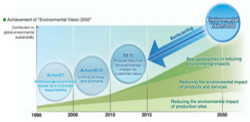
2008 Environmental Vision 2050
To do what we can to fundamentally address the deepening problem of global warming, we established Environmental Vision 2050, a document that states Epson's long-range environmental goals.
2010-2019
2010 SE15 Mid-Term Environmental Policy
Epson's SE15 Mid-Term Environmental Policy sets out the first milestones along the path toward achieving Environmental Vision 2050.

2010 New Perspective
We launched the SurePress L-4033A. This digital label press was designed with a view toward using innovative Epson products and technologies to reduce environmental impacts during use. Employing Epson's Micro Piezo technology, the SurePress offers label manufacturers a dramatically lower environmental impacts than traditional analog label presses.

2010 High-Capacity Ink Tank System
Epson began selling printers equipped with a high-capacity ink tank system in Indonesia and later expanded into some 150 countries and regions, focusing mainly on emerging nations. For this system Epson adopted a very different approach from that used in ink cartridge printers. Instead of replacing ink cartridges, users refill their printer's ink tanks with bottled ink, saving resources and providing superior environmental performance.

2012 Pursuing Compactness
To improve the basic eco-performance of our printers and to provide users with more installation options, we completely revamped the design for compactness. The Expression Premium XP-600 inkjet printer has smaller mechanisms and a new, slimmer type of print head and ink cartridge, making them significantly smaller in every dimension than its predecessor the Artisan 730.

2014 Changing Office Printing
Epson's advanced inkjet technology is driving changes in office printing by accelerating the shift from laser to inkjet.
Office inkjet printers equipped with high-capacity ink packs save resources and time by dramatically reducing the need to replace consumables, and reduce the work involved in replacing, ordering, managing, and transporting consumables inventory. And with no heat used in printing, Epson inkjets use far less power than laser printers.

2016 PaperLab released
Epson has developed technology that will change the paper cycle, give new value to used paper, and stimulate in-office recycling. The PaperLab paper recycler, released in Japan in 2016, uses Epson's original Dry Fiber Technology to securely destroy confidential documents and recycle them without using precious water resources1.
1 A small amount of water is used to maintain a certain level of humidity inside the system.

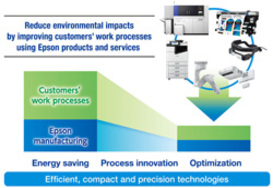
2016 Announcement of the Epson 25 Corporate Vision
We are leveraging Epson's efficient, compact, and precision technologies to drive innovations in four areas with the objective of providing products and services that reduce environment impacts, including in our customers' business processes.
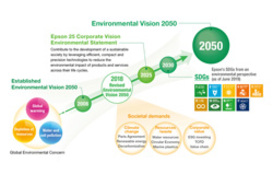
2018 Revision of Environmental Vision 2050
Responding to internal and external environmental changes, Epson revised its vision for achieving a sustainable society to reflect social imperatives. The vision articulates Epson's intention of using its unique strengths to create environmental value and address societal issues such as decarbonization, resource recycling, and the SDGs.
2018 Science Based Targets for Reducing GHG Emissions
Science Based Targets initiative has approved Epson's global greenhouse gas reduction targets as being science-based and in line with the Paris Agreement.

2019 Green Bonds
Epson formulated a green bond1 framework to procure the funds needed for projects to achieve social sustainability. We are actively using the proceeds from the issue of green bonds to advance environmental initiatives and achieve the goals of Epson 25.
1 Bonds that are issued to procure proceeds specifically for initiatives in the environmental field

2020-
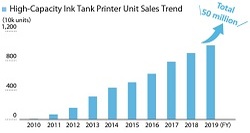
2020 High-capacity ink tank printer shipments reached 50 million units
The first high-capacity ink tank inkjet printers were launched in Indonesia in October 2010. Since then, Epson has expanded sales to some 170 countries and regions, reaching 50 million in cumulative global units. These printers use fewer materials and particularly less plastic, the main component of consumables, than ink cartridge printers.
2021 Revision of "Environmental Vision 2050
Epson's Environmental Vision was revised in conjunction with the updated Epson 25 Renewed corporate vision, which sets concrete goals for attaining our aspirational goal of achieving sustainability and enriching communities. Epson aims to become carbon negative and underground resource1 free by 2050.
1 Non-renewable resources such as oil and metals

2021 Epson 25 Renewed announced
We announced the corporate vision with the statement "Co-creating sustainability and enriching communities to connect people, things, and information by leveraging our efficient, compact, and precision technologies and digital technologies." The environment, digital transformation, and co-creation will be key to this effort. Contributions to the environment are a particular point of emphasis. On top of that, we will use digital technology and co-creation projects with a range of partners to realize innovation.
2021 Switch to 100% Renewable Electricity at Sites in Japan
Epson aims to transition to 100% renewable electricity at all Epson Group sites worldwide by 2023 on our way to becoming carbon negative by 2050. In November 2021, Epson became the first company in the Japanese manufacturing industry1 to convert to 100% renewable electricity at all its domestic sites.
1 Among Japanese companies that have joined the RE100. Per Epson research as of October 27. 2021.

2023 Partnership with WWF
Epson signed a three-year international corporate partnership with WWF, the world's leading environmental conservation organization. The partnership involves collaboration in three areas: achieving sustainable business activities, environmental communication with society, and financial support for WWF nature conservation projects. Epson supports WWF's forest conservation activities around the world through donations.

2023 Switch to 100% Renewable Electricity at All Group Sites Worldwide
In December 2023, just 2 years and 10 months after the declaration to shift to renewable electricity, the transition to 100% renewable electricity across all sites was achieved. This initiative marks the first case in the Japanese manufacturing industry1 . By continuously utilizing the most suitable natural energy sources in each region, efforts will not only contribute to achieving Epson’s goals but also foster understanding and empathy across society, thereby helping to create a social environment conducive to the widespread adoption of renewable energy.
1 Among Japanese companies that have joined the RE100. Per Epson research as of January 9, 2024.

Singapore
2025 Operations Begin at a New Plant for Recycling Used Metals
Epson Atmix, a manufacturer of metal powders, launched operations at a new metal recycling plant that recycles unutilized metals the group’s operations and the local community, using them as raw materials for the company’s metal powder products. The company’s precision technology for manufacturing high-performance metal powders contributes to the effective use of recycled materials and the efficiency of production processes, thereby helping to reduce environmental impact.




