Intellectual Property Strategy
Epson's Intellectual Property Strategy
Epson operates under a proactive intellectual property policy. Our intellectual property (IP) strategy is closely aligned with Epson's management, business, and development strategies. Our multifaceted IP activities support the growth strategy scenario. They include acquiring intellectual property rights in anticipation of future business developments, actively utilizing our IP rights, and providing IP support to achieve sustainable growth, including innovation support.
Epson's intellectual property strategy is characterized by the features below.
Value Hierarchy of Intellectual Property Activities
Epson has defined five levels in the value hierarchy of IP activities designed to convert intellectual property into corporate value. Our IP strategy is geared toward achieving Level 5, where IP activities accelerate innovation, create the future, and strengthen brand image. We believe that strong support for innovation through IP protection and proactive utilization of intellectual property based on this strategy will enhance Epson's brand identity and improve corporate value.

Epson's Intellectual Property Strategy Implementation Organization
Epson aligns its IP strategies with development and business strategies to protect its proprietary core technologies and brands. Strategies are formulated during two-party discussions between the head of the IP division and the head of each operations division and the head of the Technology Development Division or, when necessary, during three-party discussions that further include the president. During these discussions, the parties cover a range of topics. They discuss leveraging tools like IP landscapes for multidimensional investigation and analysis of technical, business, and intellectual property information to facilitate innovation support. They examine acquiring and utilizing intellectual property rights (such as patents, designs, and trademarks) to provide robust support for business and development strategies. They also address topics like digital transformation and co-creation support, as well as brand support. The aim is to report on and discuss these topics in order to align the intellectual property strategy with the overall management, business, and development strategies.
In addition, IP strategy is regularly reported and discussed at meetings of the board of directors, and the strategy is amended based on feedback from the board of directors. At a recent meeting of the board of directors, discussions were held regarding the development of intellectual property (IP) talent and the ongoing protection of core technologies that consist of a combination of patents and know-how.
Through close communication with upper management, Epson's IP strategy is configured to quickly adapt to highly uncertain and rapidly changing business environments.

This close collaboration among management, businesses, development, and the intellectual property organization is a hallmark of Epson's IP operations and an advantage when it comes to formulating IP strategy that is in lockstep with development strategy and business strategy.
At Epson, we aspire to achieve sustainability and enrich communities. Toward this end, we carry out IP activities based on multiple interconnected strategies. Our intellectual property acquisition strategy is aligned with our business and development strategies for protecting our proprietary core technology and proprietary brand from which we draw our strength. Meanwhile, our strategy of utilizing intellectual property rights is founded on the growth strategy scenario and is aligned with our business and development strategies, which are geared toward solving societal issues.
Rights Acquisition Strategy
Epson takes a proactive approach to intellectual property. We are building an intellectual property portfolio by anticipating what lies ahead and strategically, efficiently, and effectively acquiring the rights to various types of intellectual property, such as patents, design rights, and trademarks, before others.
Epson defines outstanding IP rights that elevate our competitive advantage and that help to support the growth strategy scenario as "BP" (which stands for "Brilliant iP" or "Brilliant Patents"). We are pursuing the strategic acquisition of BP in accordance with key goal indicators (KGI) set in the IP strategy. There are two categories of BP: "BP-F (fighting)" and "BP-G (guard)." A BP-F is a right that is known to be practiced by other companies and that can be utilized in the future to secure the flexibility in business operations. A BP-G is a right that significantly contributes to safeguarding the business. Epson strategically acquires "BP" based on its intellectual property strategy and integrates them into various utilizations.
At the heart of Epson's rights acquisition strategy is the filing of patent applications for inventions that accompany technology development and the acquisition of those as patent rights. Epson ranks among the world's leaders in the strategic filing of patent applications in technology fields such as inkjet printers, piezoelectric printheads as components that eject ink, projectors, robots, watches, and crystal devices. Through the strategic filing of such world-class applications, Epson has built an industry-leading intellectual property portfolio, safeguarding its proprietary technologies.

* Epson's 2024 patent registration ranking (per Epson research & excluding Chinese utility models)
Rights Utilization Strategy
Epson anticipates the future and proactively utilizes intellectual property portfolio, including BPs, in support of the growth strategy scenario. The strategy for utilizing our intellectual property portfolio is depicted in a four-quadrant chart that shows how Epson implements its patents on one axis and how our competitors implement their patents on the other axis. We formulate our intellectual property portfolio utilization strategy based on this chart, which we call a "C-Curve."

-
1. Non-licensed quadrant:In-house implementation, no implementation by other companies
Epson acquires and protects rights to core technologies that are a source of competitiveness and does not grant licenses to others.
-
2. Cross-licensing quadrant:In-house implementation, implementation by other companies
Epson tries to ensure business flexibility by entering into cross-licensing agreements with competitors who want to use our rights.
-
3. Selling and licensing quadrant:No in-house implementation, implementation by other companies
Epson monetizes rights that have contributed to the growth of business through cross-licensing agreements but are no longer essential by either selling or licensing the rights to others.
-
4. Abandonment and expiration quadrant:No in-house implementation, no implementation by other companies
Maintaining rights is costly, so Epson actively abandons rights that are unlikely to be productive.
Apart from this, Epson also utilizes its intellectual property portfolio in brand support.
An Intellectual Property Strategy That Supports Sustainable Growth
Epson acquires and utilizes intellectual property to create a positive cycle for new businesses, convert intellectual property into corporate value, and achieve sustainable corporate growth. Along with this, we engage in activities that support innovation, co-creation, digital transformation (DX), and our brands based on intellectual property.
(1) Innovation Support
IP Landscapes that guide business and development strategies
Epson supports innovation from an intellectual property perspective by using IP landscapes in conjunction with investments in startups and co-creation with third parties through open innovation. For example, in making a decision on investment in a startup company, we evaluate the value of intellectual property held by the startup company. Also, in open innovation, we use IP landscapes to capture a bird's-eye view of the current state of development and intellectual property acquisitions in a particular field and evaluate the future potential of the technology.
In addition, in order to link development themes to business growth strategies, we provide innovation support, based on analysis utilizing IP landscapes, including proposals from the intellectual property perspective, to expand the scope of application of the development themes and strengthen the underlying technologies. For commercialized development themes, the Intellectual Property Division meets with development departments/operations divisions in the two-party discussions to review evaluations of quantitative and qualitative competitive advantage based on IP landscapes. We follow that up by formulating and implementing IP strategies that stipulate the protection of intellectual property and its proactive utilization. Intellectual property at this stage includes designs, trademarks, and brands as well as patents.
Epson's Intellectual Property Division is thus providing support by implementing a strategic intellectual property strategy leveraging all types of intellectual property to accelerate the growth of its businesses through innovation arising from development themes.
The diagram on the right depicts an example of an evaluation of the patent portfolio held by Neurable, Inc., a startup engaged in Brain Computer Interface (BCI) technology development utilizing brainwave analysis. Neurable's portfolio was seen as having high value compared to the portfolios of its competitors. In April 2023, Epson X Investment Corporation, a corporate venture capital (CVC) subsidiary established by Epson, made the decision to invest in Neurable based in part on this evaluation of the value of the startup's intellectual property.
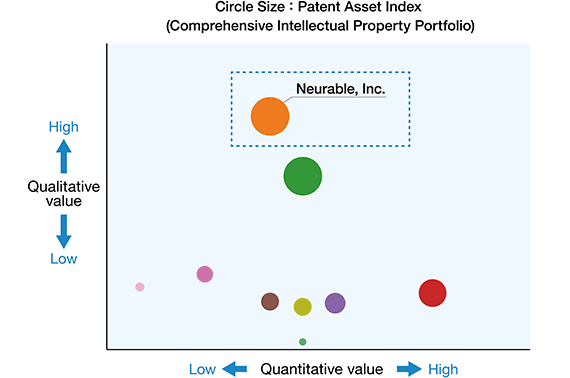
Created by Epson using LexisNexis PatentSight.
The patent asset index is a metric used to assess the total value of a company's patents.
(2) Co-creation and DX Support
Contractual support for building a co-creation scheme with partners
Rather than doing everything independently, Epson 25 Renewed, our corporate vision, emphasizes co-creation, a process in which new value is quickly created with partners who share our vision and want to work with us to accomplish it.
To smoothly advance co-creation, Epson and its partners need to put in place a business framework that benefits both parties. However, the treatment of intellectual property generated through co-creation can become a contentious issue, particularly when partnering with startup companies, and this can hinder innovation and co-creation.
We are thus putting in place the organizational support needed to expedite co-creation. Specifically, we have formed a dedicated team to support the process of drafting technology license agreements. From the moment we start exploring potential co-creation partnerships, the team will be on hand to provide one-stop support.
In recent years, we have been more deeply exploring data utilization businesses that leverage data, which is a valuable intellectual property, and businesses that utilize rapidly evolving AI. Given this, we have been categorizing data utilization businesses and AI utilization businesses, along with the type of contractual agreements for each, to enable us to more quickly execute agreements with relevant stakeholders based on these categories.
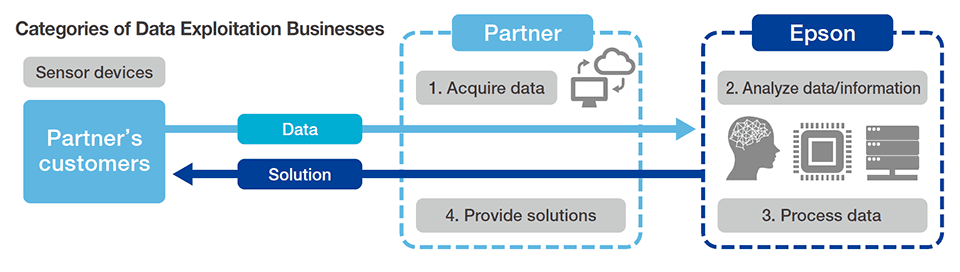
(3) Brand Support
Brand promotions that use an IP mix (sales & marketing support)
Epson utilizes a mix of intellectual properties to support its brands. This is a distinguishing feature of how Epson utilizes its IP rights.
Epson believes that building a brand requires (1) originality that differentiates the brand from the competition, and (2) constancy and continuity in conveying a consistent brand concept to customers.
(1)Epson emphasizes the originality of its product technology and designs in promotions and highlights the fact that they are protected by IP rights.
(2)Epson acquires trademark rights for its original technologies and original designs and creates technology brands and design brands around them. It uses these to continuously communicate a consistent message about the brand concept to customers.

Case Study: IP Activities Supporting Dry Fiber Technology
The Possibilities for Dry Fiber Technology
Epson is developing environmental technology to achieve the goals set forth in Environmental Vision 2050, but we believe that Dry Fiber Technology holds particular promise. Dry Fiber Technology is Epson's proprietary technology that can realize high-performance materials by defibrating paper as well as a wide variety of other fibrous materials as needed for a given application, binding the fibers with functional materials, and forming them into the desired shape. Our PaperLab in-office dry papermaking system applies Dry Fiber Technology to produce recycled paper from used paper without a large volume of water.
Dry Fiber Technology can be used in a variety of applications. For example, it is used to turn used paper ink absorbers that absorb waste ink inside our printers and into sound absorbers installed in the interior walls of equipment. Dry Fiber Technology is also being used to produce cushioning materials. Moreover, we developed new packaging material made from cotton scraps produced in the process of garment manufacturing, which we have been using as packaging material for watch products. Meanwhile, Epson is promoting open innovation for application to fields in which we have limited knowledge. With a view to helping establish a circular economy, for example, in order to promote greater scope in the use of bioplastics and recycled plastics, we are working on joint research on a molding technology using fiber-composite plastic materials that combine cellulose fibers generated with Dry Fiber Technology and plastic materials with the aim of solving issues such as the strength and durability of bioplastics and recycled plastics. We are also promoting joint research to establish a technology to defibrate fibers that are difficult to recycle with the aim of providing a new recycling solution for cloth.
IP Activities Supporting Dry Fiber Technology
Building a patent portfolio
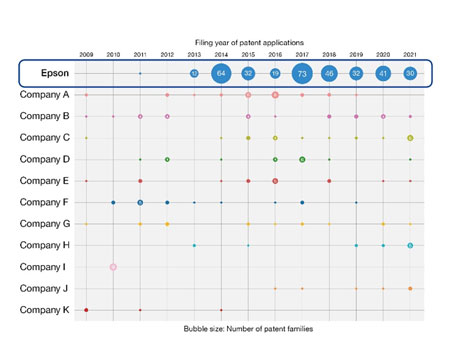
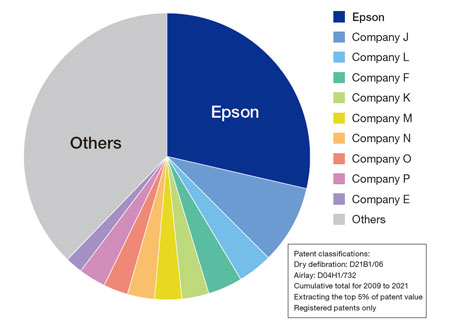
In developing a patent portfolio, the Intellectual Property Division and the Development Department confirm a quantitative and qualitative assessment of our competitive advantage through IP landscapes in the two-party discussion, after which an IP strategy aligned with the development activities is determined. Dry Fiber Technology is a technology with a competitive edge from an IP perspective as well. In order to boost the competitive advantage of businesses based on Dry Fiber Technology, Epson has been making patent applications in the field constantly since the early days of its development based on an IP strategy and has built a powerful patent portfolio which overwhelms other companies in terms of quantity. Moreover, Epson ranks top in the ownership ratio of high-quality patent families in the Competitive Impact of patent families in the field. This indicates that we have built a powerful patent portfolio for Dry Fiber Technology in terms of both quantity and quality based on our IP strategy.
Number of patent applications filed by year in the Dry Fiber Technology field1
Ownership ratio of the top 5% of patent families in the Dry Fiber Technology field in terms of Competitive Impact1
1 Graphs created by Epson using LexisNexis PatentSight
Epson is working to enhance its corporate value by earning external recognition and prestigious honors, such as the National Commendation for Invention, to demonstrate to the public that our technology has a competitive advantage. With respect to Dry Fiber Technology, Japanese Patent No. 6127882 from our powerful patent portfolio received the Asahi Shinbun Award in the 2019 National Commendation for Invention2. This patent relates to double-stage sieving, one of our core Dry Fiber Technologies. This award made it clear, through evaluation by an external organization, that Dry Fiber Technology is making a considerable contribution to the promotion of science and technology and the development of industries and economy.
2 For more information, please see the "Organization and External Recognition" page.
Supporting innovation through IP landscapes
In working to generate bioplastics through Dry Fiber Technology, we proposed, based on an analysis using IP landscapes, multiple development plans which have potential and compatibility with our technologies with limited barriers in terms of Intellectual Property held by other companies to the development department, to work as development theme on our own. Thus, we are using the IP landscapes to support the creation of new innovations in Dry Fiber Technology.
NDA support for co-creation schemes with third parties
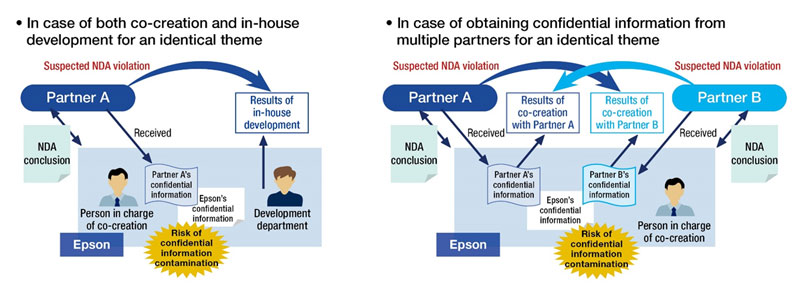
Epson is promoting various open innovations centered on Dry Fiber Technology concurrently. What becomes the key in doing so is the management of confidential information which is an important information asset of our co-creation partners. The contamination risk of confidential information is heightened, in particular, when we have co-creation with an identical theme under way concurrently. In order to mitigate the risk, we not only develop a template for a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) for co-creation but also establish our thinking as a guideline and communicate it thoroughly within the company. We consider agreements for the purpose of developing good relationships with co-creation partners as important IP and seek to raise the legal awareness of our employees, working in cooperation with the Legal Department.
Branding of technology
Technologies are intangible assets whose value is difficult to appreciate unless you are a technological expert. Therefore, we acquired a trademark right that sums up the technological features of Dry Fiber Technology to get its technical name recognized by our customers to promote branding of the technology. By displaying the Dry Fiber Technology trademark in a variety of situations, we increase our customers' recognition of our technical name and their value.



